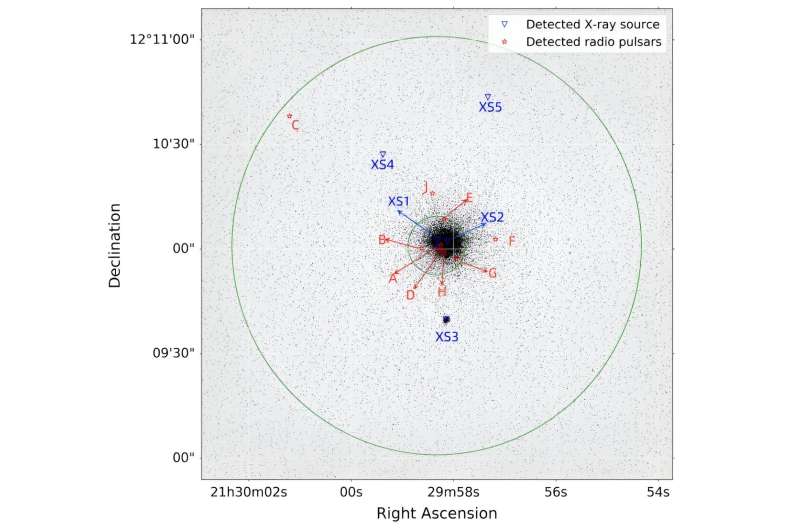
Pulsar position and X-ray source position in Messier 15. Image Source: arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2312.06067
Astronomers used China’s 500-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST) to discover three new pulsars in the ancient galactic globular star cluster Messier 15. Two of them are long-period pulsars, while the remaining one is spinning very fast. It was soon classified as a millisecond pulsar. The findings were reported in a paper posted on a preprint server on December 11 arXiv.
Pulsars are highly magnetized rotating neutron stars that emit beams of electromagnetic radiation. The fastest rotating pulsars, whose rotation period is less than 30 milliseconds, are called millisecond pulsars (MSP). Astronomers believe they form in binary star systems when the initially more massive component becomes a neutron star and then spins up due to the accretion of material from the secondary star.
Located approximately 35,700 light-years from Earth, Messier 15 (also known as NGC 7078) is a core-collapsed GC with a radius of approximately 88 light-years and an estimated mass of 560,000 solar masses. It is one of the oldest (approximately 12 billion years old) and most metal-poor galactic GCs (metallicity approximately 2.25), and one of the densest GCs in the Milky Way.
Previous observations of Messier 15 have detected nine pulsars, the first of which was discovered in 1989. According to simulations, Messier 15 may be one of the GCs with the highest number of pulsars. That’s why a team of astronomers led by Wu Yuxiao from Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications in China decided to use FAST to conduct a pulsar search in this cluster.
The newly discovered pulsars are named PSR J2129+1210J, PSR J2129+1210K and PSR J2129+1210L. Observations found that PSR J2129+1210J is an MSP, while the other two are long-period pulsars.
Research shows that PSR J2129+1210J is an isolated pulsar with a rotation period of approximately 11.84 milliseconds and a measured dispersion value of 66.68 pc/cm3. PSR J2129+1210K has a rotation period of approximately 1.93 seconds and a dispersion of 68.01 pc/csm3.
PSR J2129+1210L has a rotation period of 3.96 seconds, making it the pulsar with the longest rotation time currently known in the GC. The dispersion of this pulsar is measured to be approximately 67.1 pc/cm3.
The researchers note that the precise locations of PSR J2129+1210K and PSR J2129+1210L are still unknown, but they are likely not too far from Messier 15’s core. Therefore, further observations are needed to find their exact locations, which will help determine whether they are young or recycled pulsars.
More information:
Yuxiao Wu et al. used FAST to discover three pulsars in the globular cluster M15 (NGC 7078). arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2312.06067
Journal information:
arXiv
2023 Science X Network
citation: FAST detects three new pulsars in old globular clusters (2023, December 20), Retrieved December 21, 2023, from https://phys.org/news/2023-12-fast-pulsars – globular-cluster.html
This document is protected by copyright. No part may be reproduced without written permission except in the interests of fair dealing for private study or research purposes. Content is for reference only.
#FAST #detects #pulsars #globular #clusters
Image Source : phys.org